MIMS Education

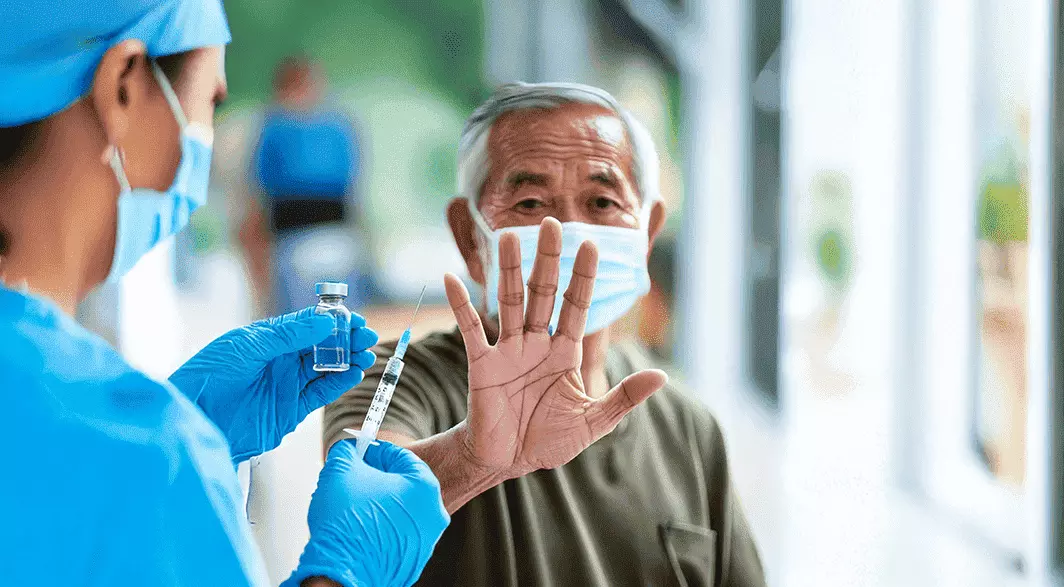
Addressing Vaccine Hesitancy in Older Adults: Effective Communication Strategies for Physicians
Overview
About this course
Vaccination is recognized as one of the most essential and cost-effective approaches for the primary prevention of infectious diseases. The benefits associated with vaccination demonstrate the crucial role of vaccines in maintaining individual and public health.
Globally, the number of older adults is expected to increase by more than twofold by the year 2050. With the aging population's increased susceptibility to vaccine-preventable diseases, life-course immunization should be advocated by healthcare professionals. Vaccine hesitancy, a global health threat, is a significant barrier to adult vaccination. There are several factors as to why patients refuse to receive vaccines despite their availability. Understanding the contributing factors to vaccine hesitancy can improve physicians’ approach to addressing this widespread issue.
Physicians can help mitigate vaccine hesitancy through employing effective communication strategies. This would entail the use of presumptive language and motivational interviewing techniques, and personalization of patient communication. Collaborative training programs, such as improvisational theater technique, aid physicians in practicing purposeful and respectful conversations with unvaccinated patients. Overall, tailored communication can significantly improve success of vaccination efforts.
This e-learning module aims to equip physicians with the knowledge and strategies to address vaccine hesitancy effectively and promote vaccine uptake among older adults.
Learning outcomes
Upon completion of this module, learners should be able to:
- Recognize the importance of vaccination among older adults.
- Understand vaccine hesitancy and the underlying factors that contribute to it.
- Address vaccine hesitancy through application of effective communication strategies.
- Promote older adults’ confidence in receiving vaccinations.
Topic covered:
- Introduction
- Understanding Vaccine Hesitancy
- Effective Communication Strategies to Address Vaccine Hesitancy
- Educating and Engaging Healthcare Professionals
- Building Patient Confidence in Vaccination
- Training Program for Healthcare Professionals
- Combatting False Information Beyond the Clinic
- Case Scenarios
Speakers for this module:

Dr. Asok Kurup
Infectious Diseases Physician
Mount Elizabeth Hospital, Singapore
Chair, IHH Antimicrobial Resistance Advisory Committee

Dr. Megat Mohamad Amirul Amzar
Bin Megat Hashim
Family Medicine Specialist
Pusat Perubatan University Malaya
1 CPD Point Available
- Score at least 80% on the quiz.

